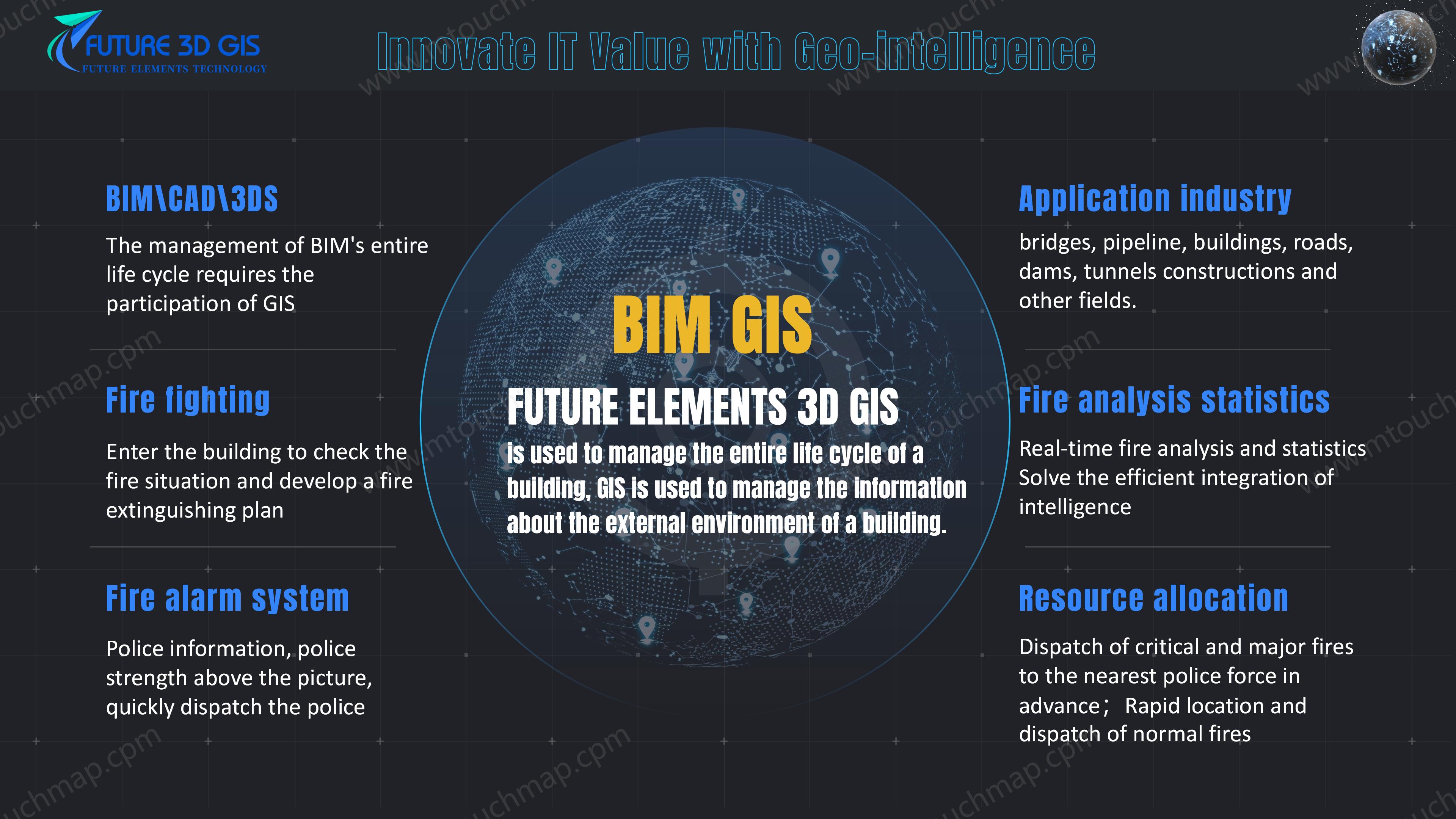
BIM+GIS
FUTURE ELEMENTS TECHNOLOGY PTE is an innovative GIS platform software and service provider,Innovate IT Value with Geo-intelligence.
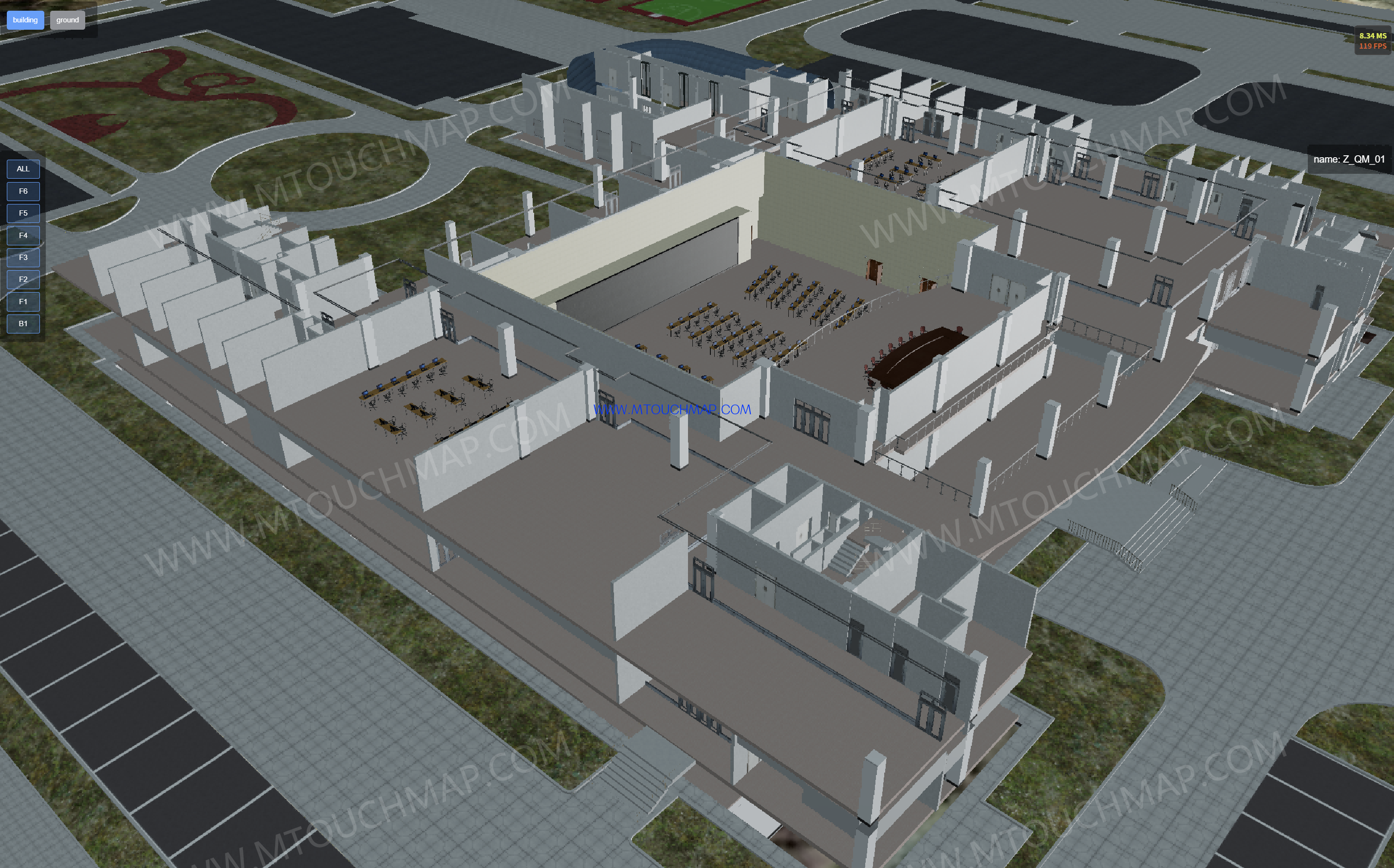
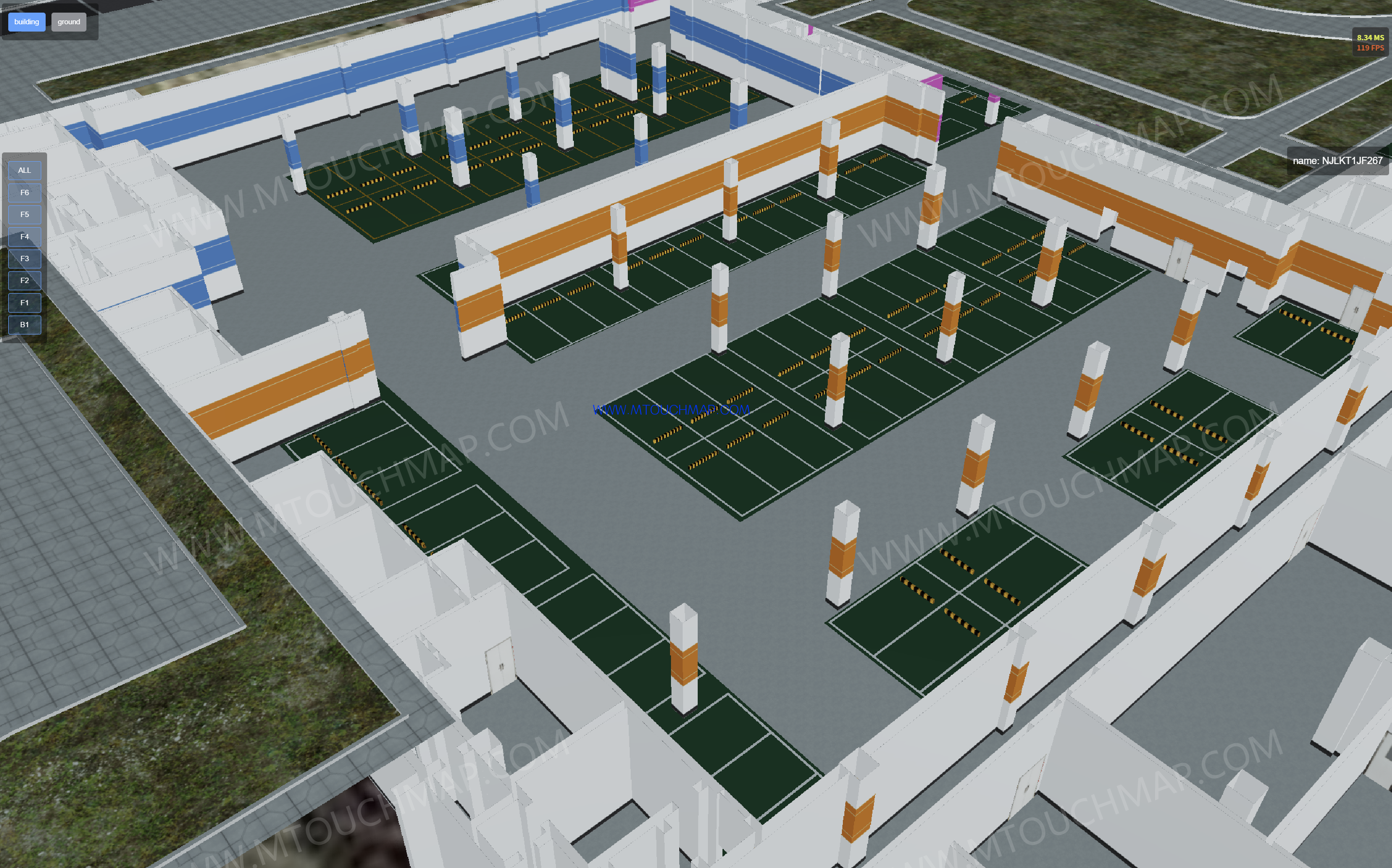
BIM+GIS:BIM (Building Information Modeling) provides detailed three-dimensional geometric models and rich attribute information of buildings, including structure, systems (such as electrical, plumbing, HVAC), materials, and construction progress, focusing on the full lifecycle management of the building itself. GIS (Geographic Information System), on the other hand, excels in managing macro-level geospatial data such as terrain, land use, road networks, urban infrastructure layouts, and surrounding environments, offering capabilities for location-based and spatial relationship analysis Key applications include:
Urban Planning and Management: Integrating multiple BIM buildings into urban GIS to support overall planning and 3D visualization.
Facility Operation and Maintenance: Leveraging GIS spatial analysis to optimize building equipment management and maintenance.
Emergency Response: Quickly locating buildings and utilizing their internal structure to assist in disaster response and rescue.
Construction Management: Analyzing the relationship between construction sites and surrounding geographic environments to improve construction organization efficiency.
Core Value: Achieving the integration of information from the "micro" level of buildings to the "macro" level of regions, enhancing comprehensive management and decision-making capabilities.